Neonatal jaundice - Neonatal jaundice: Cochrane evidence on prevention and treatment
Recent Posts
- Washing machine heart lyrics
- New world order 2013
- 100 000 rupiah to myr
- Ankle boots
- Sb dunk
- Tarikh bayaran i citra september
- Idiyappam
- Switch sungai petani
- Kl tower ticket price 2021
- Destini share price
- Jaya bachchan young photo
- How many people died from coronavirus
- India vs new zealand
- Kuih yang boleh dimakan ketika berpantang
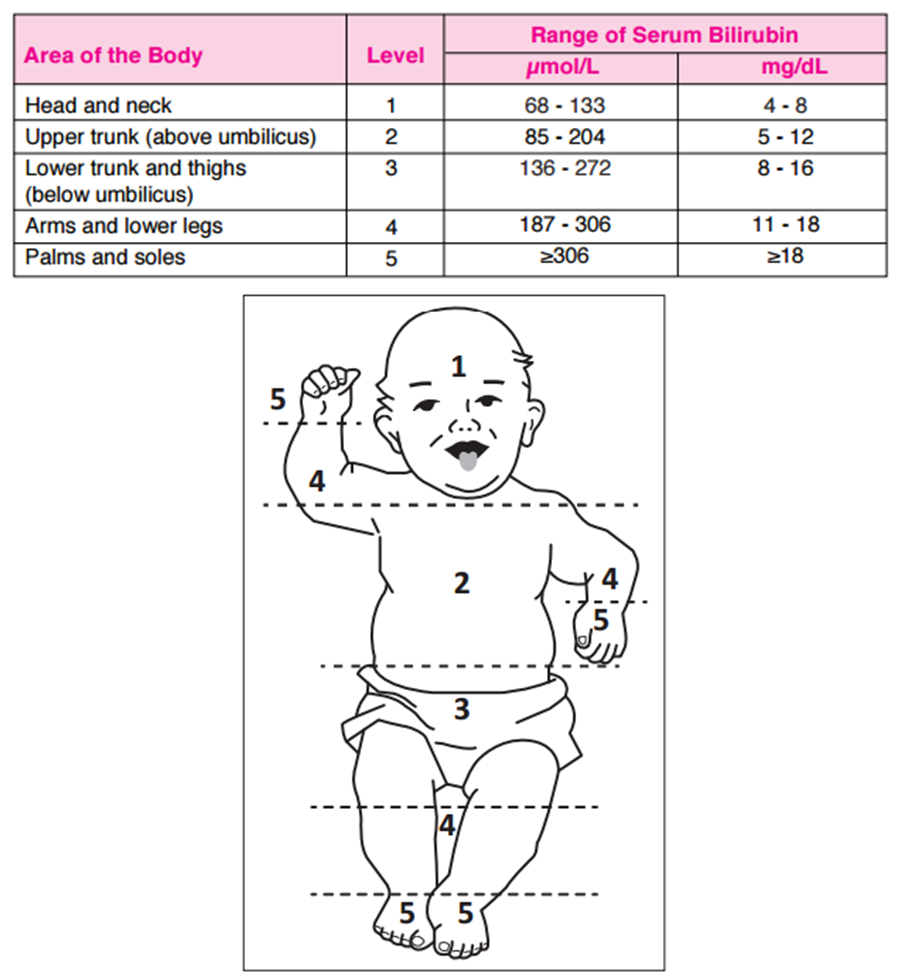
neonatal jaundice, classification and diagnosis
Acute bilirubin encephalopathy Bilirubin is toxic to cells of the brain.
Newborns should be examined within 24 to 72 hours of hospital discharge to assess for jaundice and general well-being.
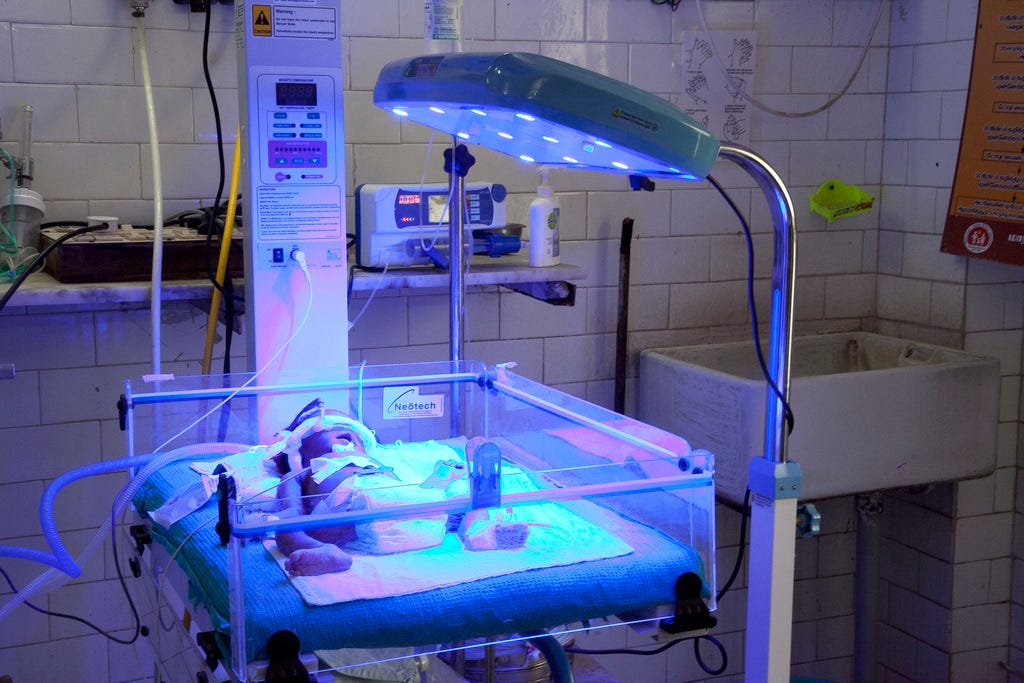
Its effectiveness is related to the area exposed, radiant energy, and wavelength 400-500 nanometers.
Neonatal Jaundice Management
It occurs because of physiological changes taking place during the transition from intrauterine to neonatal life.
Early damage to the brain can be reversible but if hyperbilirubinemia is pronounced or prolonged then it can lead to cerebral palsy, sensorineural hearing loss or cognitive impairment.
Merck Manuals Professional Edition.
- Related articles
2022 blog.dabchy.com